12 tweaks to make your Windows PC lean, mean, and fast
If the storage space on the C drive is running low, every free gigabyte counts. Windows often occupies more than 25 GB of space for things such as updates, restore points, and cache files. Plus, pre-installed bloatware further increases memory utilization. Freeing up memory can quickly become critical on notebooks with 128 GB SSDs or devices with soldered memory. But even on well-equipped systems, it’s worth decluttering Windows as it can lead to fewer processes, a faster startup, and lower CPU load.
Caution: Not every measure is risk-free. If you remove system components or libraries too aggressively, Windows may become unstable, updates may fail or programs may refuse to work. You should therefore always work with a restore point, back up your Windows installation and choose your methods carefully. Some changes can be undone immediately, others require a new installation.
Table of Contents
Quick start: Delete temporary files and update remnants
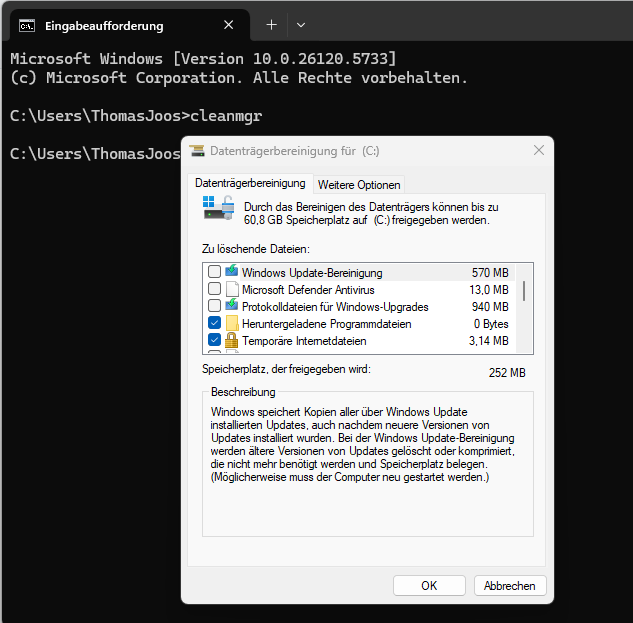
Start with the on-board function “Disk cleanup” and also click on “Clean up system files”. Open it via “cleanmgr” in the command prompt or in the properties menu of the C drive. Activate all tick boxes here including “Update cleanup”. Be sure to avoid “Downloads” if you are still using the folder. Also, you can empty the “Recycle Bin” without hesitation.
Thomas Joos
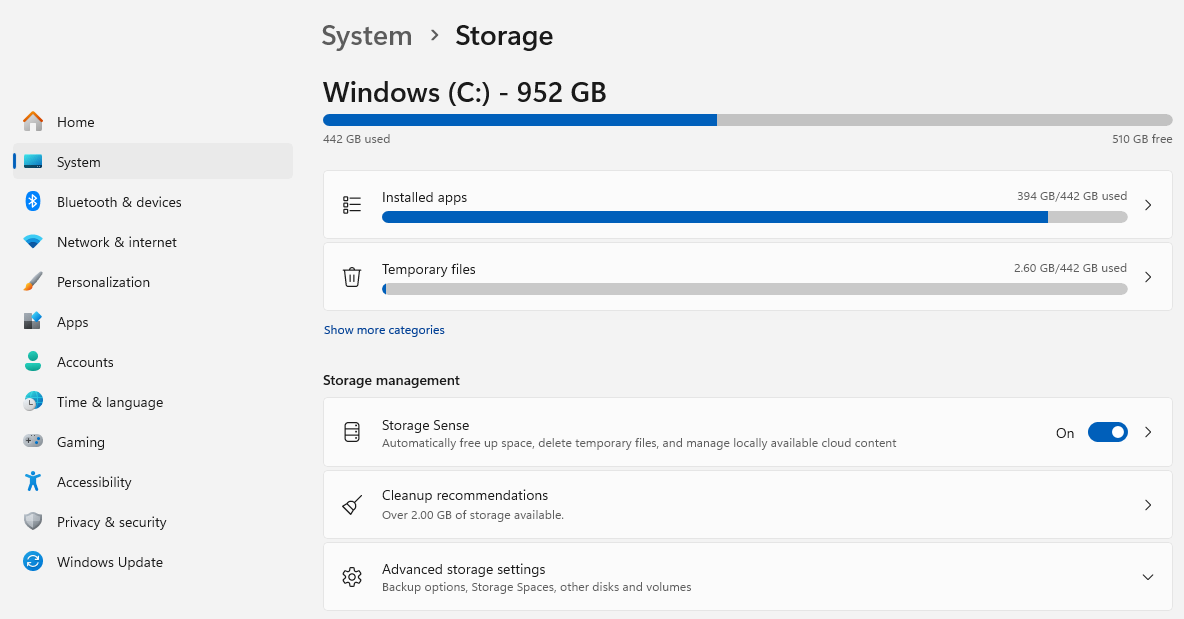
In addition, open “Settings”, navigate to “System -> Memory -> Memory optimization” and activate automatic clean-up. You can also control the behavior for other drives via “Advanced storage settings”. In combination, all of these will results in you quickly gaining several GB of space.
Sam Singleton
Delete search index and remove update buffer
The Windows Search Index might not be commonly known, but it’s often several gigabytes in size. The “Windows.edb” file is located under “%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows” and grows over time. If you’re already working with the “Everything” tool, you can deactivate the Windows search service and delete the file.
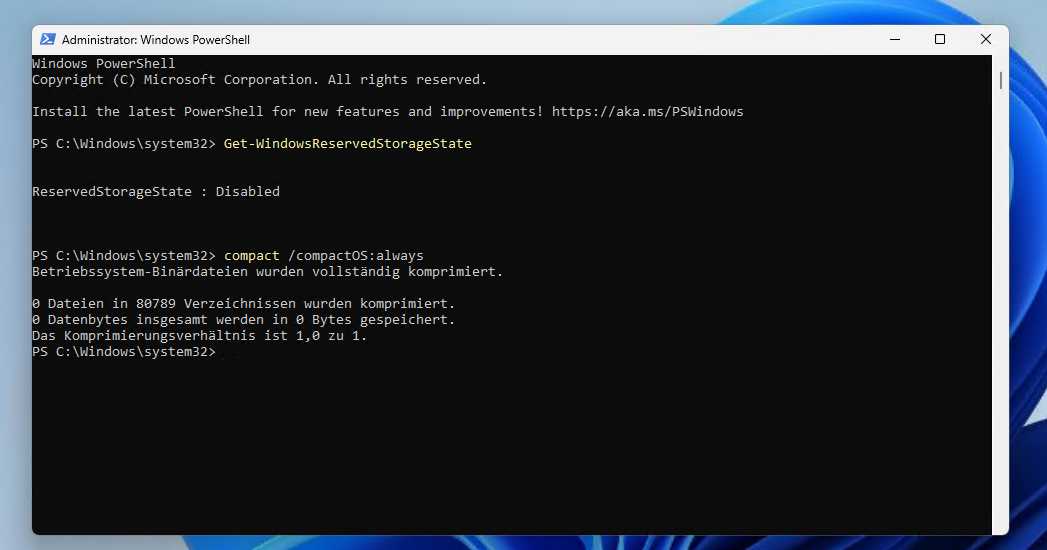
Windows also reserves up to 7 GB for future function updates by default. If you want to reclaim this space, open Powershell with administrator rights and execute the command “Set-WindowsReservedStorageState -State Disabled -Online“. The change only works if no maintenance processes are currently running. If an error message appears, wait until Windows has completed all updates.
Thomas Joos
The shared memory will then remain available, but future updates will require sufficient free space in the active file system.
Compressing system files with CompactOS
A powerful and often underestimated command: “compact /compactOS:always” is used by Windows to compress all system files without any loss of functionality. The space gained is between 2 and 6 GB. The command works from Windows 10 onwards and can be cancelled at any time with “compact /compactOS:never”. Use “compact /compactOS:query” to check whether the function is already active.
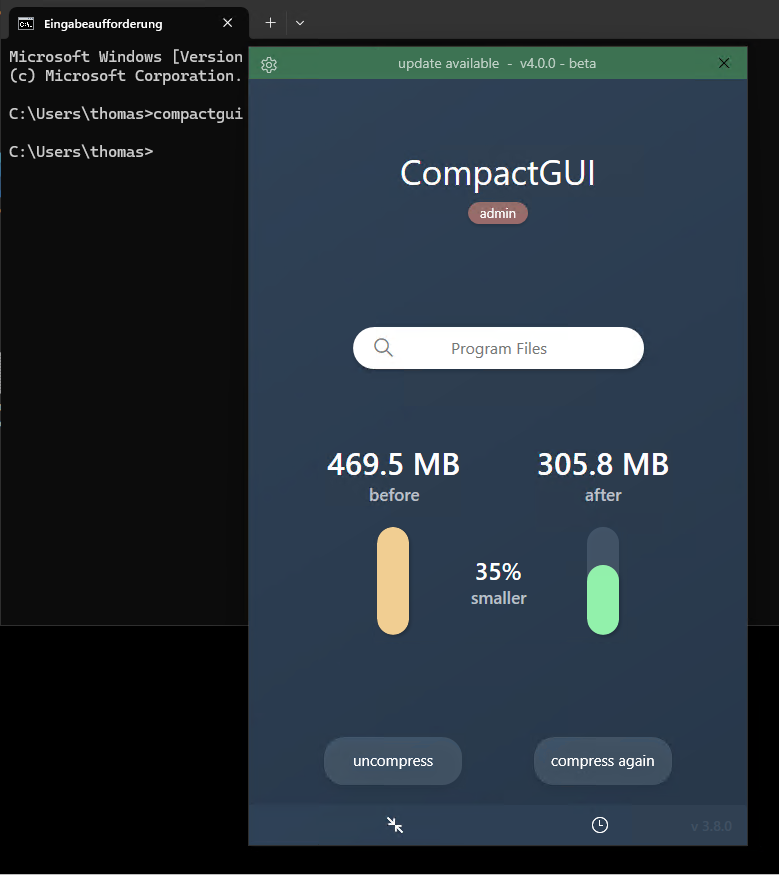
For targeted compression of individual folders, use CompactGUI or Compactor. Both support various algorithms such as LZX or Xpress16K and also work stably with large directories.
Thomas Joos
While CompactGUI relies on the familiar “compact.exe” backend and integrates itself into the Explorer menu with an intuitive interface, Compactor uses the Windows API directly and therefore offers some additional functions. For example, the tool analyzes the data blocks before compression and intelligently decides whether a file can be compressed at all, eliminating pointless operations on incompressible files.
A small hash database remembers these cases permanently, which significantly speeds up subsequent runs. Compactor also shows (in real time) how much storage space is actually freed up by each individual step, including a pause and resume function while compression is running.
Both tools offer a choice of compression algorithms. XPRESS4K works the fastest, LZX offers the highest reduction. Especially in game directories or with software such as Visual Studio, Adobe products or SDKs, space savings of 40 to 60 per cent can be achieved with LZX. The developer of Compactor documents typical results directly on GitHub – from 2.4 GB to 1.4 GB for AI War 2 or from 9.6 GB to 4.7 GB for Visual Studio.
It is important to note that the programs remain fully functional as the compression is transparent. All files can be opened or executed as usual without having to be decompressed first.
However, you should note that certain formats such as SQLite databases or virtual machines do not harmonize well with Windows compression. DirectStorage-based games under Windows 11 should also be excluded, as the decompression step cancels out the advantage of the direct connection to the GPU. If you want to be on the safe side, use the integrated exclusion lists and check all critical programs after the first run. System folders such as “C:\Windows” are automatically ignored.
Both CompactGUI and Compactor are portable and do not require installation. For Compactor, we recommend the 64-bit version directly from the GitHub release area. After the first start, the tool can be used without logging in, all processes run locally. Compactor compresses reliably, quickly and with minimal CPU load – even on older systems.
Windows 11 without ballast: using Tiny11 correctly
Tiny11 is a modified Windows 11 installation without the need for TPM, an online account and bloatware. The latest version based on Windows 11 24H2 uses only 3.5 GB with LZX compression, less than a DVD. You can either obtain Tiny11 via the Internet Archive or create your own ISO with the Tiny11 Builder. This is how it works:
- Create a new directory, such as “C:\t11”.
- Download the “Source code (zip)” archive from GitHub.
- Mount the Windows ISO by right-clicking on “Mount”.
- Open “Powershell (Administrator)”.
- Enter: “Set-ExecutionPolicy unrestricted”.
- Change to the directory with “cd \t11” and execute: “.\tiny11maker.ps1”.
- Enter the drive letter without “:” (e.g. “E”).
- In the next step, select “Windows 11 Pro” (e.g. option 5).
- You will then find the new ISO under “C:\t11\tiny11.iso”.
Copy this to a USB stick using Rufus. Important: Deactivate all settings in the “Windows user experience” dialogue. Install the system offline to create a local account.
WinUtil: Preconfigured images with minimal effort
If you don’t just want to slim down Windows, but want to start it completely preconfigured and without any setup procedures, you can use WinUtil by Chris Titus. The tool creates automated minimal images with a local account, without a TPM check, without online connection and with only half the memory requirements of a regular Windows.
Thomas Joos
Even more radical: Tiny11 Core and slimmed-down VHD installations
The Core version of Tiny11 also removes Windows Defender, Windows Update and recovery mode. Activate this profile with “.\tiny11coremaker.ps1”. This variant is extremely lightweight, but cannot be updated.
Alternatively, install Windows directly on a virtual hard disk (VHD). The WinNTSetup tool creates a bootable VHD that you can use like a normal system, ideal for experiments.
You can also run the Win11Debloat tool. It specifically removes apps such as Xbox, Onedrive, Cortana or Edge. If you want to go even further, use Win Reduce. Here, individual system folders such as “WinSxS” or “System32” can be greatly reduced in size, but be careful as the system can no longer be updated afterwards. The configuration is carried out via text files in the format “remove-” and “keep-“.
Note: this procedure is only suitable for experts or test environments.
Win10XPE and PEbakery: Build minimal Windows yourself
If you want to start an ultra-light Windows without installation constraints and with portable apps, Win10XPE is the right choice. The project is configured using the PEBakery tool. The goal is an ISO file that runs completely in RAM, ideal for emergency use or old hardware.
Thomas Joos
For desktop integration, place portable accessories such as Firefox or LibreOffice in “Custom\x64\IsoRoot\Programs”. Optionally, mount the target folder as drive Y via “CDUsb.y”. The ISO can be tested via VirtualBox or written to USB with Rufus.
Reinstall Windows without ballast, legally
If you want to completely do without a customized version, use NTLite. The tool loads the ISO, removes apps, services and language packs and adds updates or drivers if required. It then creates a new, clean ISO. This gives you a legal Windows setup, customized exactly to your requirements.
WinScript offers a graphical interface with functions for app removal, optimization of data protection, performance, and gaming options. Select “Debloat”, remove Candy Crush, Xbox Game Bar or Feedback Hub. Under “Privacy” and “Telemetry”, you can deactivate diagnostic transmissions, advertising IDs and other background services. The software creates a restore point before every action.
Further tips with a direct effect
- Remove the hibernation file with “powercfg -h off” to save up to 4 GB.
- Move the swap file to another drive with “sysdm.cpl ,3”.
- Reduce the system protection memory with “sysdm.cpl ,4” → “Configure”.
- Avoid deduplication of updates by switching off the transfer optimization under “Windows Update” → “Advanced options” → “Transfer optimization”.
This article originally appeared on our sister publication PC-WELT and was translated and localized from German.